自然语言处理期末重点
自然语言处理期末重点
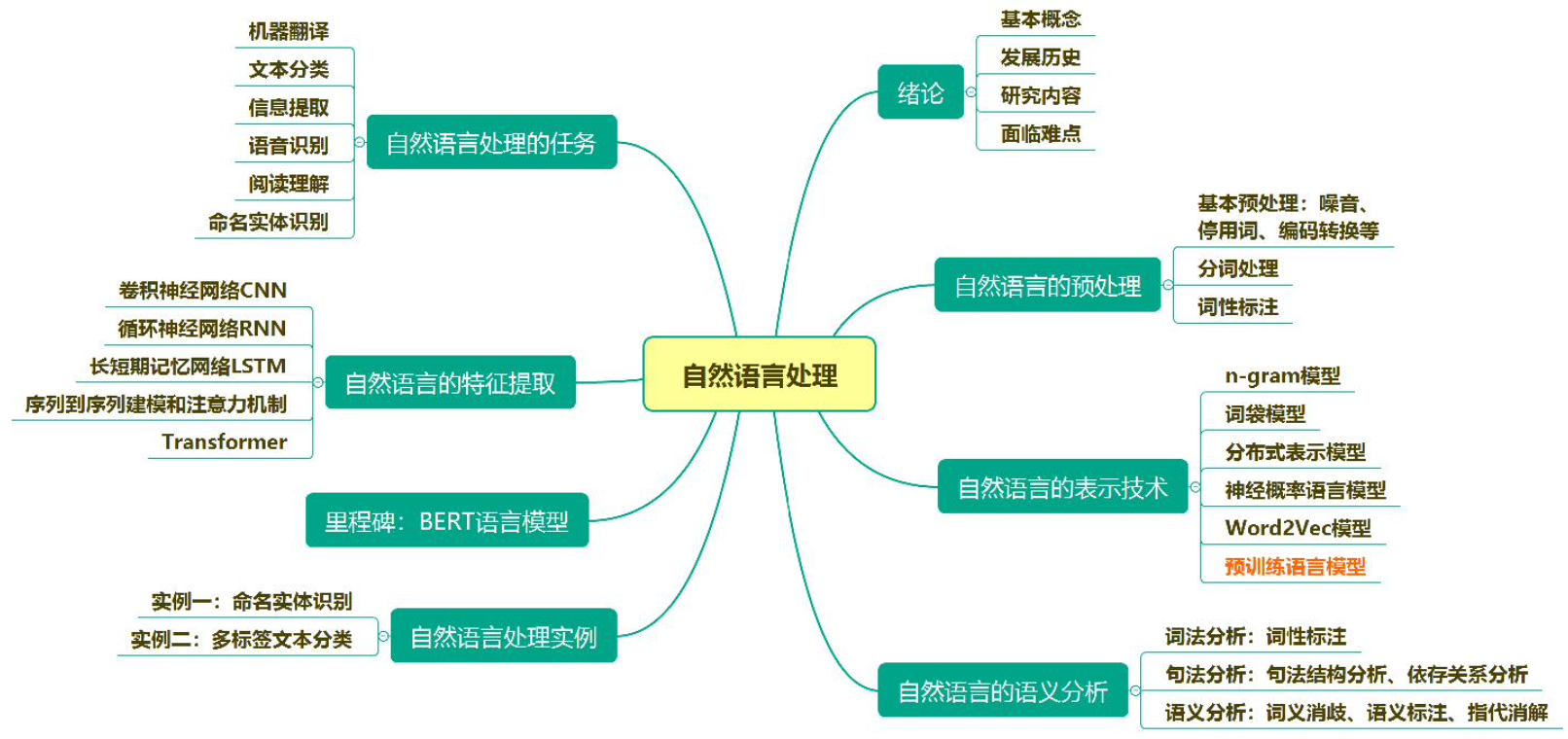
CH1 绪论
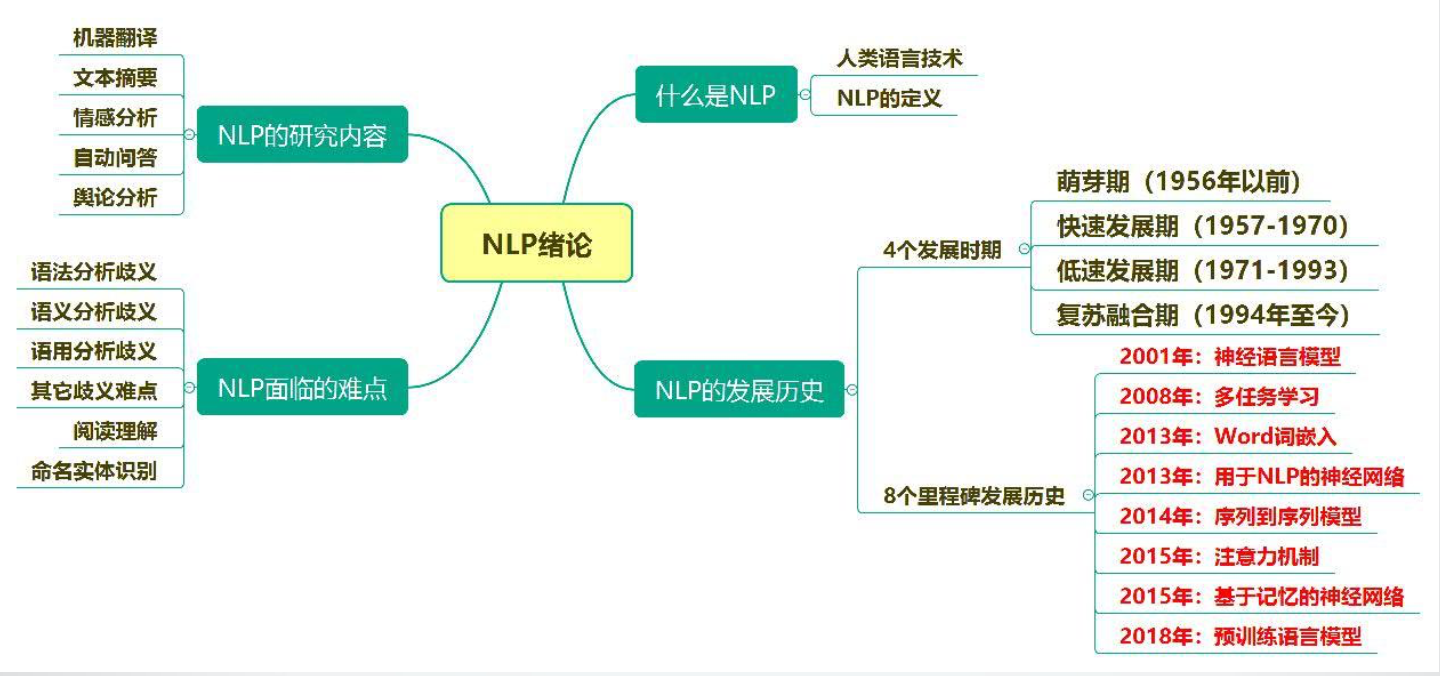
1. 自然语言处理定义



自然语言处理既是科学,又是技术。
2. 面临难点
歧义问题:词法分析歧义、语法分析歧义、语义分析歧义、语用分析歧义、分词歧义、词性标注歧义、命名实体识别歧义。(具体例子见ppt)
本质是知识体系缺乏。
对策:建立“知识”(规则方法、经验方法、规则经验结合、交互式处理)、减少“未知知识”(限定语言、领域、任务、复杂度)
3. 四个发展期、八个里程碑
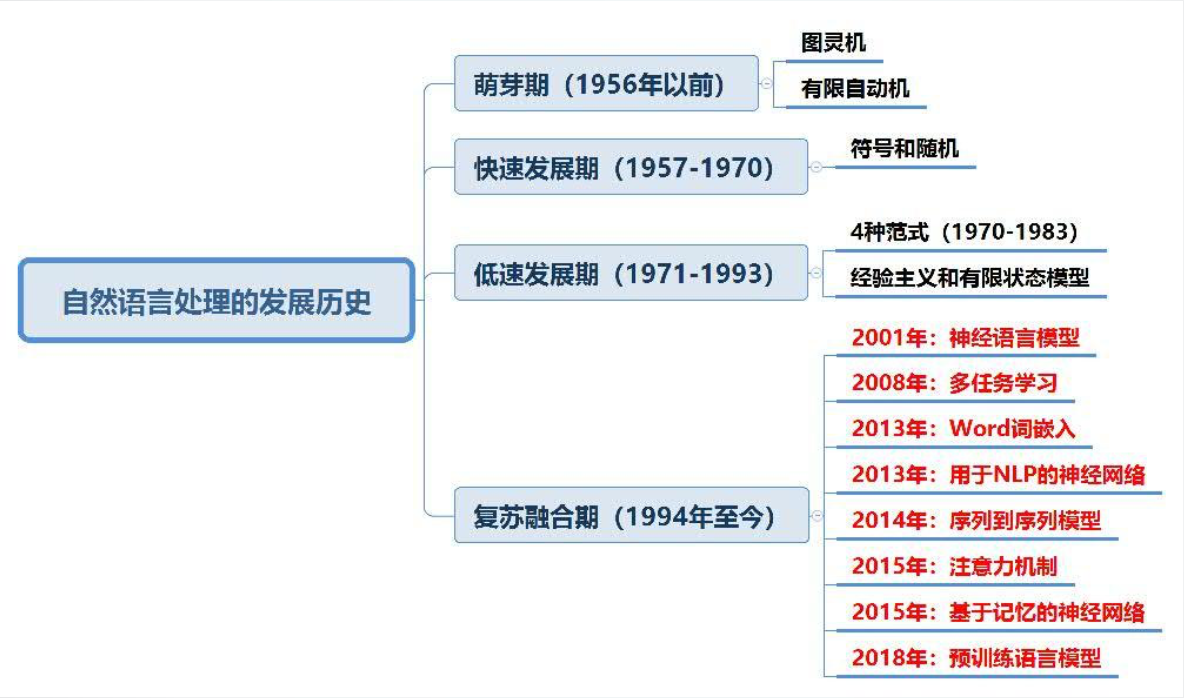
具体见上图及ppt
CH2 预处理
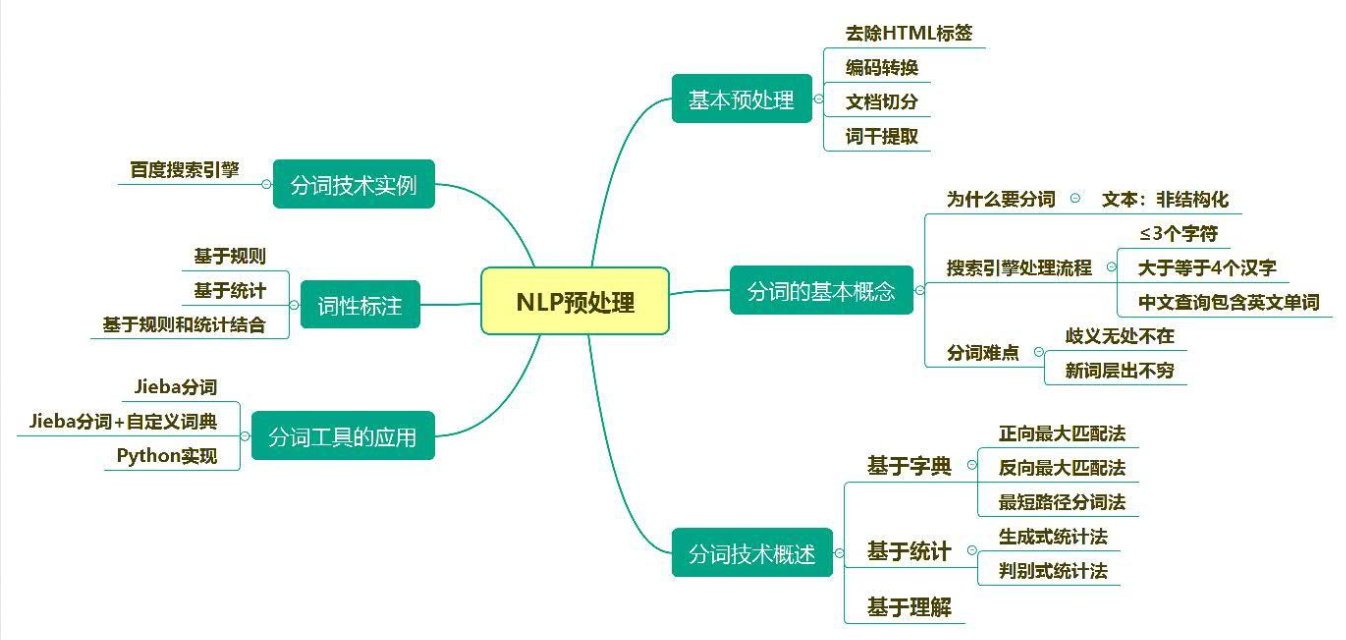
1. 预处理的原因及内容


2. html定位元素
#数据解析
# //相对路径 找到所有
tree = etree.HTML(page_text)
div_list = tree.xpath('//section[@class="list"]/div')
for d in div_list:
title = d.xpath('.//div[@class="property-content-title"]/h3/text()')[0]
# title = d.xpath('./a/div[2]/div/div/h3/text()')[0]
3. 分词
(1) 整体难点
新词层出不穷、普通词与新词互用、普通词与新词交织在一起、需求多样化
(2) 三种方法
a. 基于字典
按照一定的策略将待分析的汉字串与一个充分大的词典中的词条进行匹配,若在词典中找到某个字符串,则匹配成功。 常用方法:正向最大匹配、反向最大匹配、最短路径分词。
b. 基于统计
相邻的字同时出现的次数越多,越可能构成一个词。常用方法:生成式统计分词(首先建立学习样本的生成模型、再利用模型对预测结果进行间接推理。)、判别式统计分词。
c. 基于理解
通过让计算机模拟人对句子的理解,达到识别词的效果。
d. 优缺点
基于词典的,部署比较简单,只需要安装词库即可。实现也简单,对比查找词语库的思路。 缺点是,分词精度有限,对于词典里没有的词语识别较差。
非词典分词法,优点是,对于出现过的词语识别效果较好,能够根据使用领域达到较高的分词精度。 缺点:实现比较复杂。前期需要做大量的工作。
4. 词性标注
(1)基于规则

(2)基于统计模型
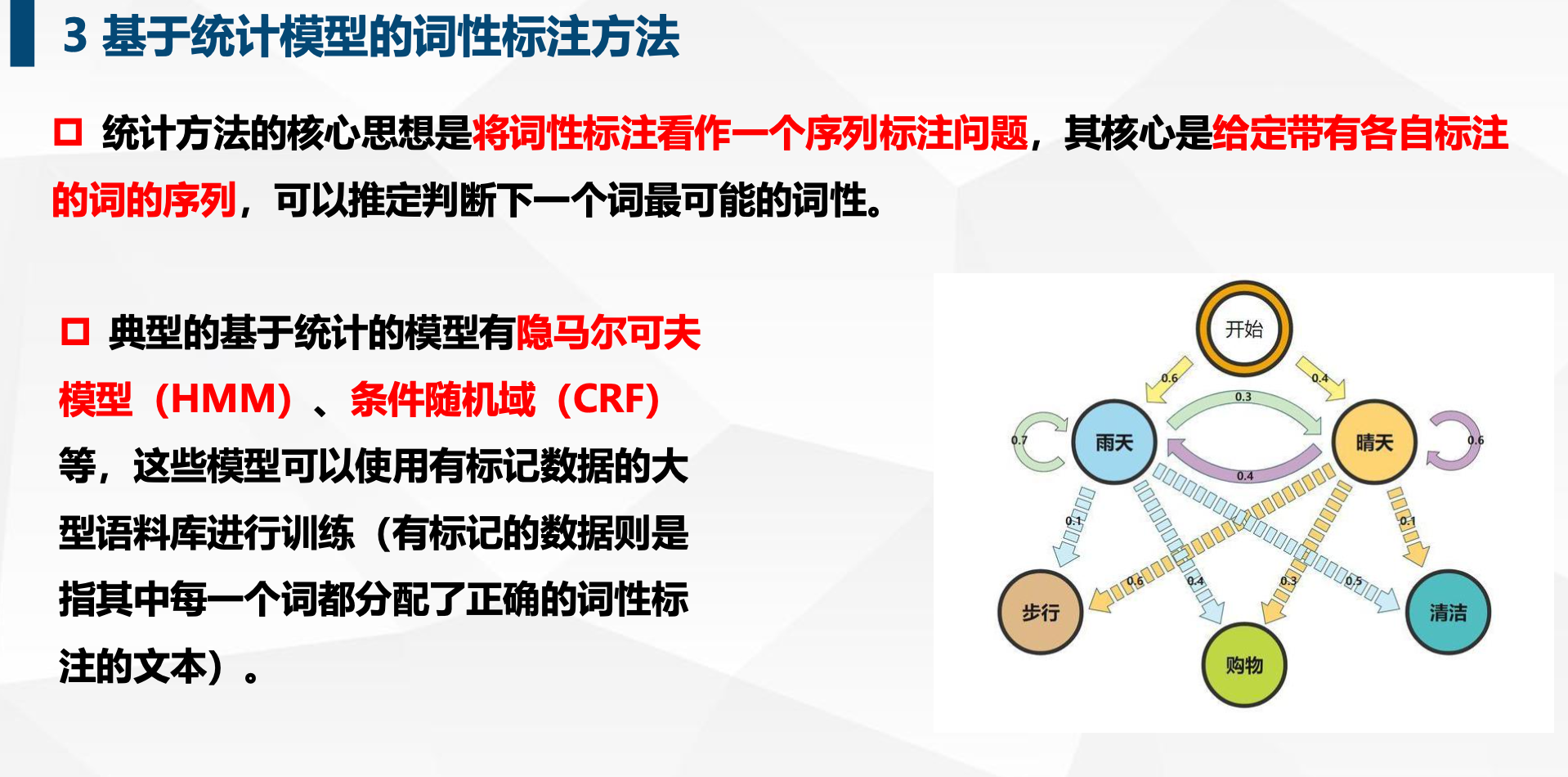
(3)基于统计与规则相结合

CH3 文本向量化(上)
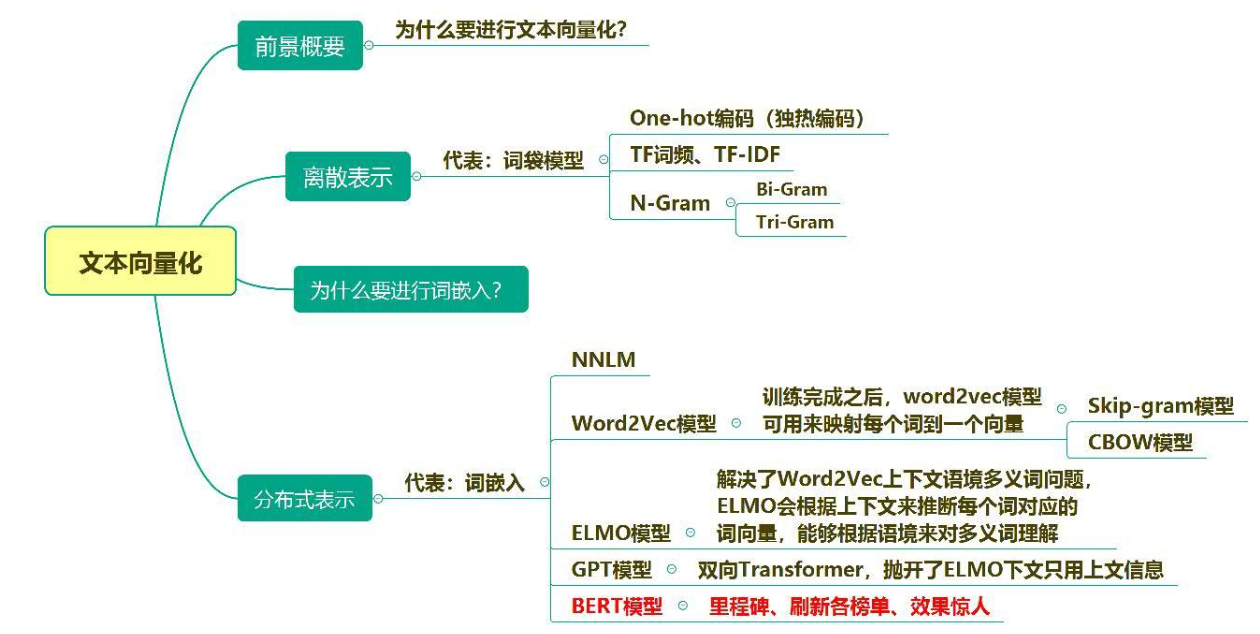
1.文本向量化原因
文本表示是自然语言处理中的基础工作,文本表示的好坏直接影响 到整个自然语言处理系统的性能。文本向量化就是将文本表示成一系列能够表达文本语义的向量,是文本表示的一种重要方式。
2. 文本向量化方法(离散表示:词袋模型)
(1)Onehot
统计各个词在文本中是否出现,出现则表示为1,未出现表示为0。向量维度为N维。
(2)TF(词频)

(3)TF-IDF(词频-逆文档频率)
逆文档频率的大小与一个词的常见程度成反比

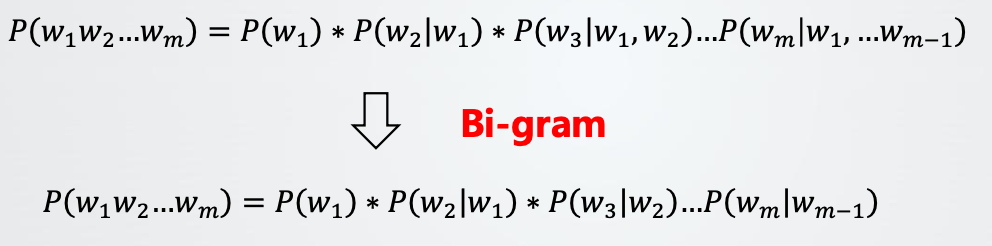
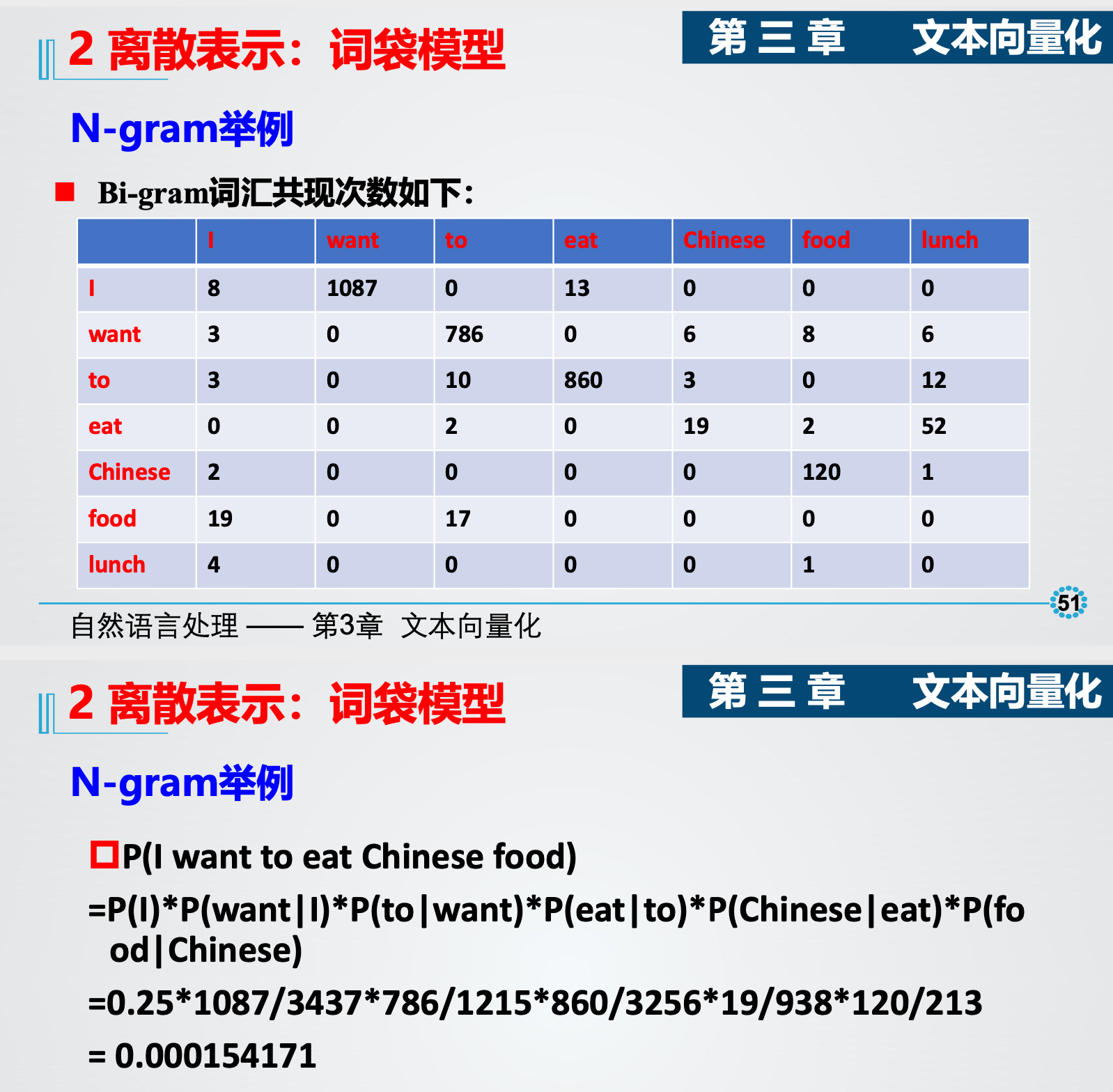
(4)Ngram
3. 词袋模型存在问题
维度灾难、无法保留词序信息、存在语义鸿沟
4. 词嵌入
将词映射到一个维度较小的向量空间内,进而利用统计学方法来研究词与词之间的关系。相比于词袋模型,降低了词向量的维度,减少训练所需数据量。
5. NNLM(神经网络语言模型)
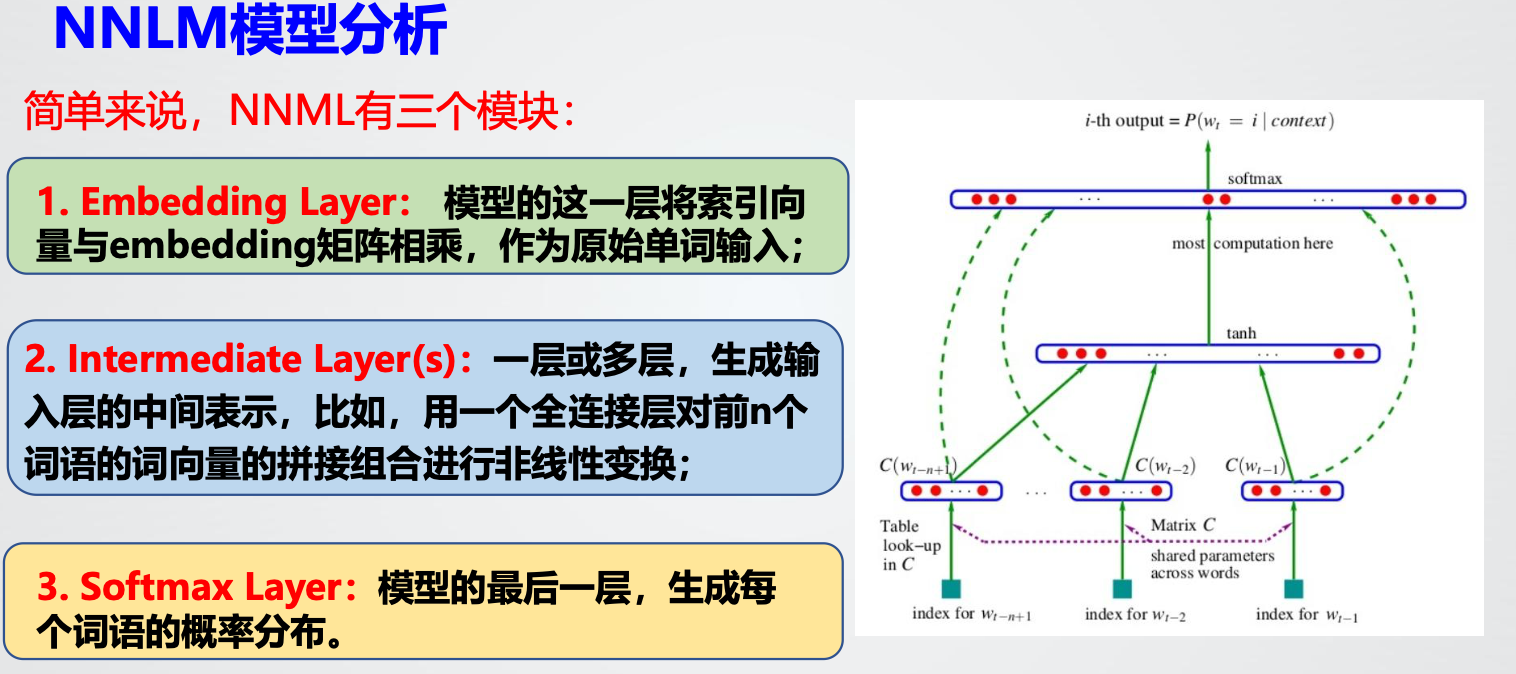
输入向量在隐藏层和输出层中都被使用。
存在问题:同样仅包含了有限的前文信息,计算复杂度较大,参数较多。模型优化不够,输出的类别较多导致训练过慢;自回归语言模型,无法获取下文信息;
CH4 文本向量化(中)
1. Word2vec两种结构
CBOW、Skip-Gram
区别仅仅是输入层、输出层不同、参数优化的指导依据不同
2.Word2vec存在问题:一词多义
总结见ppt
CH5 ELMO
1.全称、要点
ELMO(Embedding from Language Models)

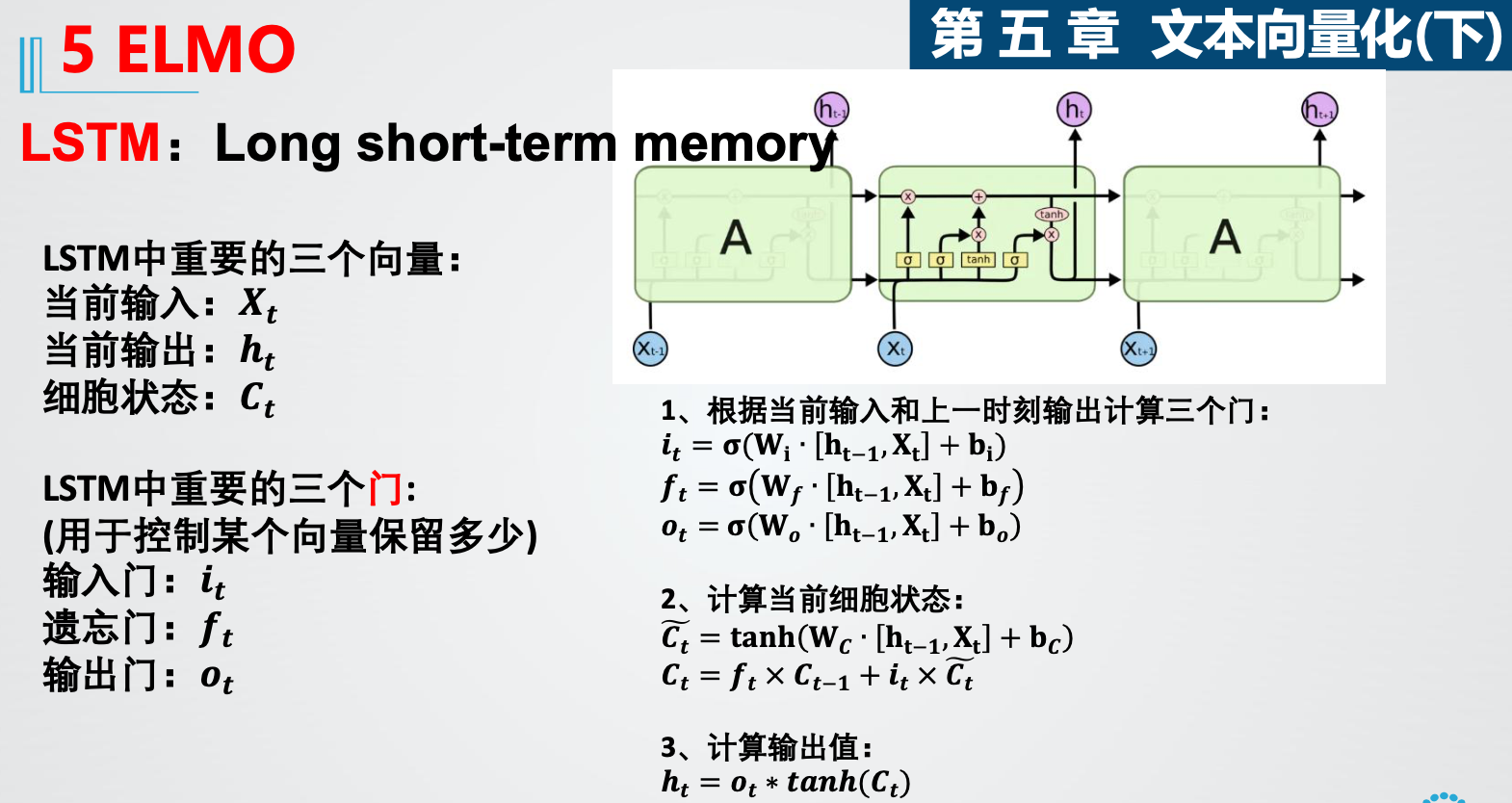
2. LSTM 三个门
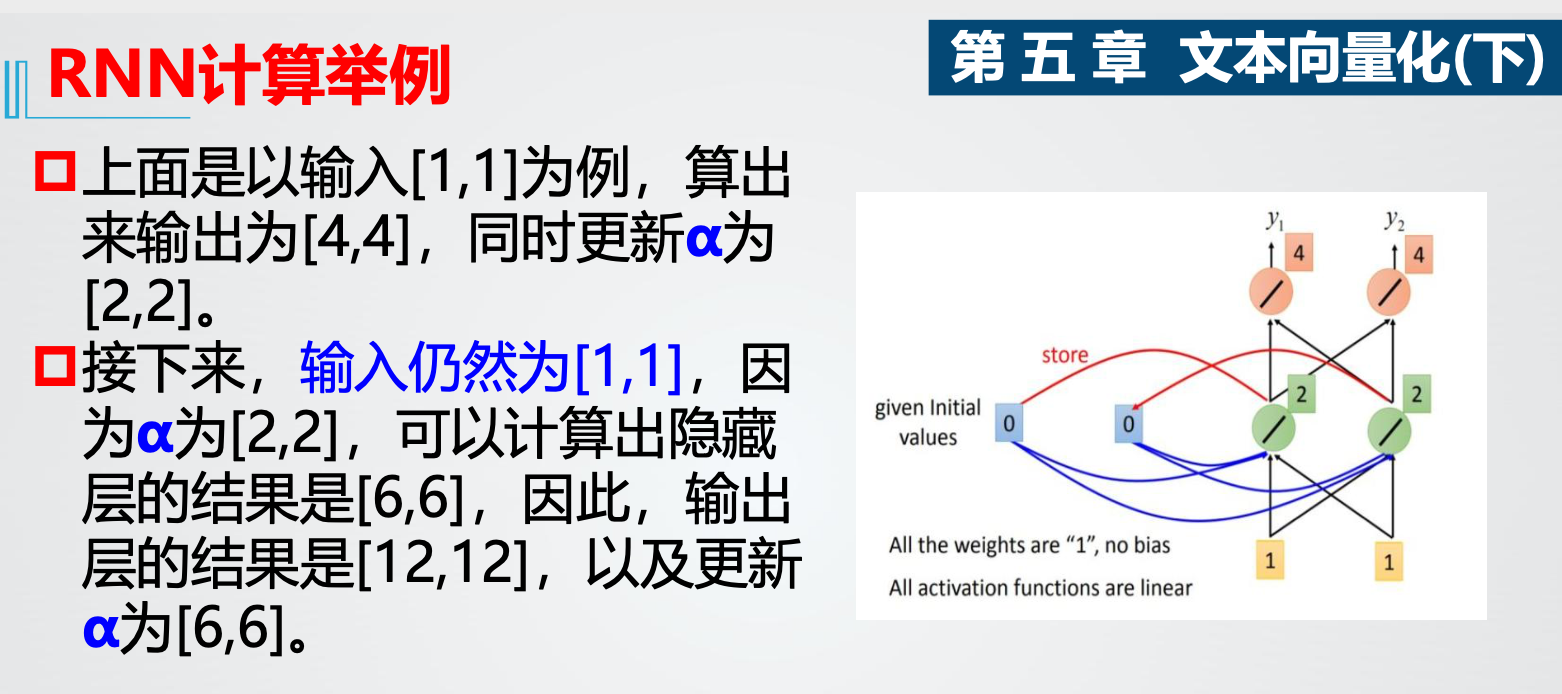
3.RNN结构 计算

CH6 GPT
1.定义、优势、改进方向
GPT(Generative Pre-Training)生成式预训练
两阶段:利用语言模型进行预训练、通过Fine-tuning解决下游任务。
与ELMO对比:
GPT只采用上文进行预测,ELMO采用上下文
特征抽取器:GPT采用Transformer,ELMO采用RNN
不足之处:
单向语言模型,没有把单词的下文融合进来
改进方向:
微调与特征融合